UC Merced Achieves Carbon Neutrality
The University of California, Merced is proud to announce it is the first public research university in the nation, and the first institution in the University of California System to achieve Carbon Neutrality.
Since the founding of UC Merced in the San Joaquin Valley in 2005, a commitment was made to demonstrate environmental stewardship.
This commitment is grounded in the pioneering spirit of our campus, reflected in academic, engagement, and operational programs.
Course offerings like sustainable energy and earth systems sciences have integrated sustainable learning in the classroom. Co-curricular experiences and internships like the UC Bonnie Reiss Carbon Neutrality Student Fellowship Program have allowed and continue to allow our students to explore ways to reduce climate impacts.
Our staff, faculty, and students have contributed to resource conservation through participation in institutional practices like centralized printing stations in buildings that eliminate individual printers.
Our operational infrastructure encourages efficiency through single system optimization, and energy load shifting. While the use of renewable energy reduces emissions.
The actions taken by our campus have been steps toward building solutions for tomorrow. Many of these actions demonstrate how resource demand can respect nature's fragile abundance.
These efforts are some of the actions that reduced UC Merced's carbon emissions profile and serve as a reminder that we can confront the climate crisis through collective action.
At UC Merced, sustainability is about building on progress to date.
We are just getting started.
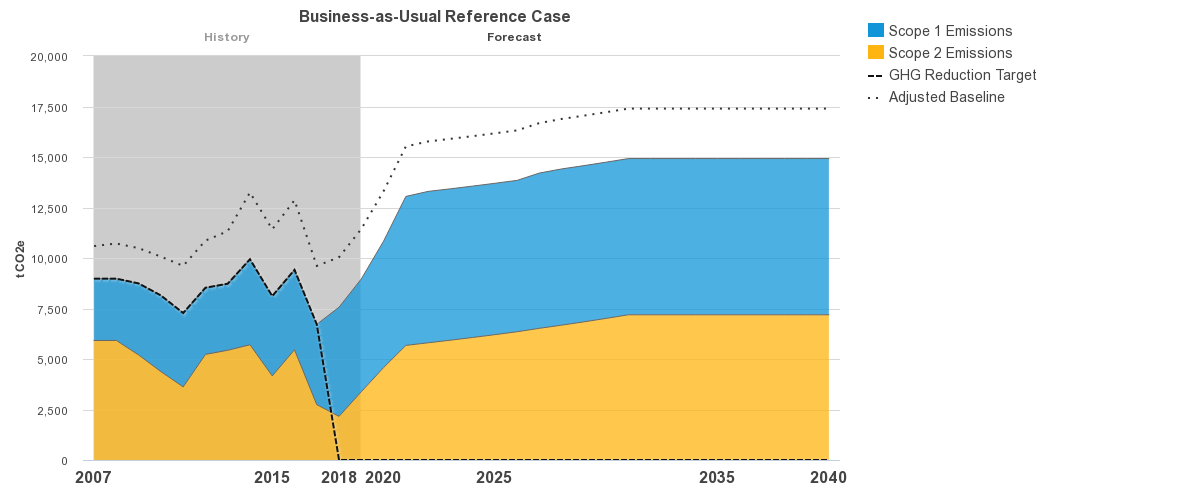
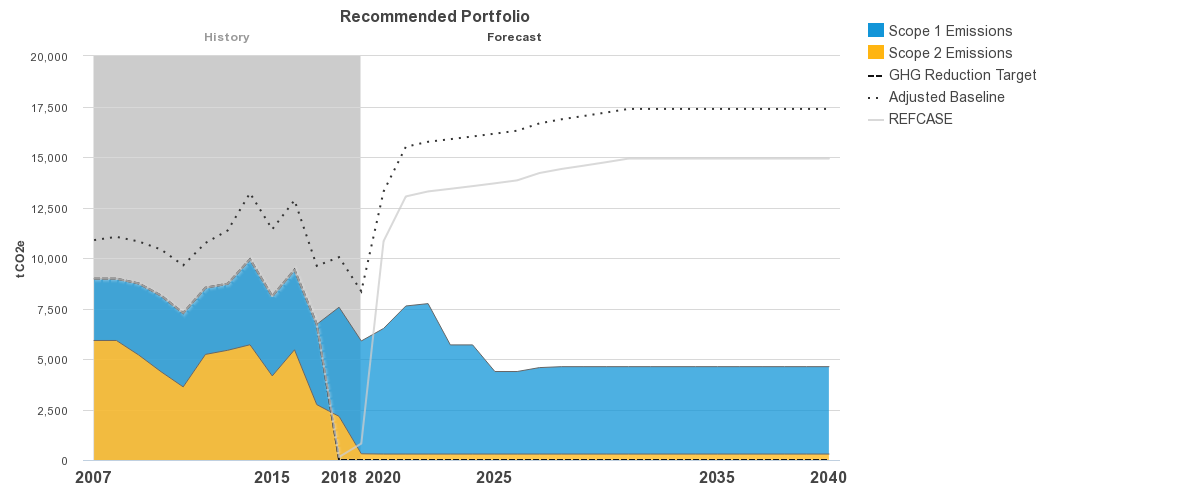
The University of California Office of the President (UCOP) Energy & Sustainability division has been a tremendous support in UC Merced's efforts to achieve carbon neutrality. The campus began using FOVEA Software, a resource provided by UCOP to evaluate campus emissions and inform campus portfolio and technical approaches to achievement. The graphs above reflect UC Merced's operational emissions that account for university facilities located on and off the campus. The business-as-usual graphic illustrates historical and future projected carbon emissions for UC Merced if the campus did not take measures to reduce its emissions profile. The recommended portfolio depicts actual historical and projected emissions with the integration of current and future actionable measures taken by the campus. The contrast of colors noted in both graphics distinguish scope 1, onsite fossil fuel combustion (blue), and scope 2, purchased electricity (orange) emissions. As reflected in the recommended portfolio, scope 2 emissions have been eliminated through onsite renewable energy and campus participation in the University of California System Wholesale Power Program, which provides clean electricity to various UC campuses. The opportunities presented for the campus will be to identify alternative renewable sources for fossil fuel combustion.
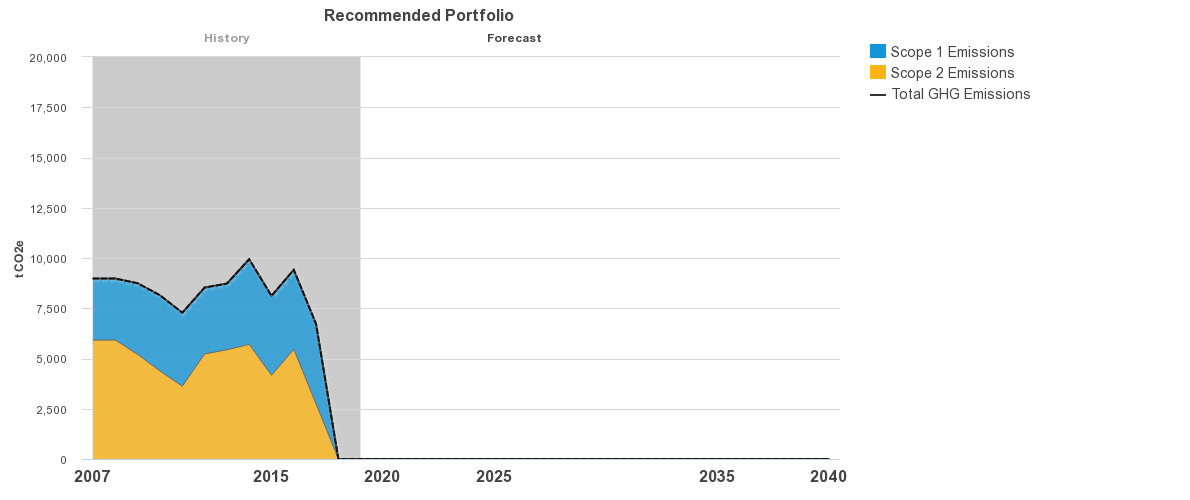
The graphic above reflects UC Merced's carbon emission profile through current and future strategies. The campus has also worked to move offsite utility accounts to our energy service provider to supply a cleaner electrical mix to the campus. Seven accounts were processed in 2019.
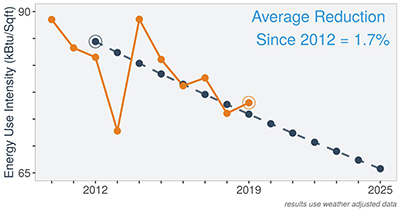
As a measure to reduce energy use intensity (eui) the UC Sustainable Practices Policy specifies that campuses in the University of California System would reduce energy use toward Carbon Neutrality goal achievement. Over the span of UC Merced's history, the campus energy use intensity has varied while maintaining a level eui over the past five years. In 2018 three new campus buildings opened, while the campus was able to reduce its eui. With two added academic research facilities in 2019 and full building loads from 2018, there was a moderate increase in 2019 eui. The campus engagement and programmatic initiatives are essential strategies the campus has taken to reduce and encourage eui reductions.
FAQ Community Engagement High-Performance Buildings Energy Efficiency Projects Educational Strategies Renewable Energy More Projects Transportation Offsets Research
FAQ
What is climate change?
Climate change is the long-term alteration of weather patterns over time. Traditionally, climate change is a natural process that occurs as a result of complex interactions between radiant energy from the sun, Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and landmasses. However, the current warming trend that is observed across the globe is anthropogenic, or human-induced. Since the Industrial Revolution, the burning of fossil fuels such as oil and coal has dramatically increased the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide among other greenhouse gases. The increase in the atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases has exacerbated the greenhouse effect, which traps heat close to the surface of the Earth. Failure to significantly cut down carbon emissions, alongside cuts to other greenhouse gases puts critical infrastructure, public health, labor productivity, and ecosystems around the world at risk.
What is Carbon Neutrality?
Carbon Neutrality at UC Merced is achieving zero net greenhouse gas emissions for scope 1 and scope 2 emission sources. This can be done through a combination of energy-efficient design, renewable energy generation, offsets, occupant behavior changes, and clean power.
What is carbon dioxide?
Carbon refers to carbon dioxide emissions (CO2e) which are typically released through natural processes and human-induced activities that include fossil fuels and deforestation.
How does carbon contribute to climate change?
With increased human-induced CO2e levels, more heat on the Earth causes vast changes in weather patterns that contribute to the frequency of droughts, fires, catastrophic storms. There is a natural process of healing from the Earth but the rate relative to human-caused emissions output is deepening.
What emissions is the campus neutralizing?
Scope 1 and scope 2 emissions. Scope 1 emissions are directly generated through the combustion of fossil fuel on campus including natural gas, gasoline, as well as fugitive. Scope 2 emissions are generated through the purchase of power from utilities.
Community Engagement
The university community, students, faculty, and staff hold an important role in UC Merced's carbon neutrality initiative. The Office of Sustainability worked to solicit feedback on priorities and strategies intended to build on existing values, policies, and practices that inform climate action planning and strategic planning. Through community engagement, educational outreach programs were developed to encourage our campus community to integrate sustainable practices into workspaces, laboratories, and student accommodations.



Continued campus-wide engagement is ongoing through the Chancellor Advisory Committee, the Faculty Advisory Committee, and the Student Sustainability Council. These committees work together to identify projects and programs that prioritize carbon emissions reduction through behavior change and institutional culture.
Programmatic Strategies
Did you know that outside of a building's design, occupant behavior, plug loads, and process loads can account for upwards of 30% percent of a building's energy use? These programmatic engagement initiatives aim to integrate healthy sustainability practices across all areas of our campus, and are important to engage our campus community to reduce building energy use.
Green Offices: works with departments, units, and offices to integrate sustainability practices into workspaces. The program assesses a department's efforts in some of the following areas: energy and climate, waste and recycling, purchasing, outreach, and events. Participants have assisted our campus by reducing energy use, waste, and sourcing sustainable products. Qualifying departments are certified under one of the following levels: Bronze, Silver, Gold, or Platinum.



Green Labs: the program works with individual PI's and researchers to inform and assess areas of improvement around sustainability and efficiency in research, including targeted initiatives to source energy-efficient equipment and reduce waste.



EcoRep Program: Focuses on sustainable living using peer education techniques to inform students on practices they can incorporate into their lives and student accommodations.



LEED LAB: is a multidisciplinary course that spans over two semesters where students work on the certification of buildings under LEED Existing Building Operations Maintenance (EBOM). The program has allowed students to assess the operation and maintenance of buildings and submit these findings to the USGBC. To date, three buildings have been certified under LEED EBOM through the LEED Labs program.


Cool Campus Challenge: The Cool Campus Challenge was a friendly 4-week challenge within the University of California system in 2019 designed to educate and motivate campuses to take simple energy-saving, waste reducing, sustainability-focused actions to reduce the campus community's carbon footprint and help the UC system reach carbon neutrality by 2025. The Cool Campus Challenge called for UC campuses to spend the month of April pledging to reduce their carbon footprints. UC Merced reduced its greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (C02) by more than 2.3 million pounds through the sustainable actions promoted by the competition. Student organizations and campus departments created more than 35 teams, and the university had the largest carbon-emissions savings per participant, with the greatest percent participation compared to the population within the system.


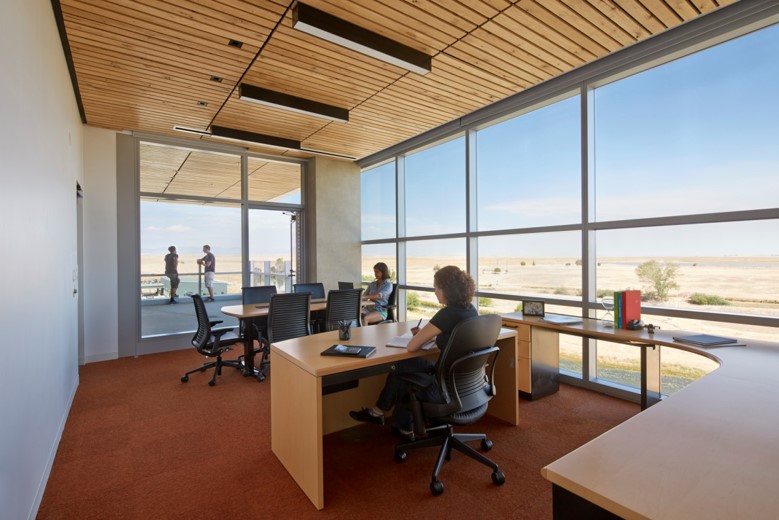
High-Performance Buildings
The campus market-leading energy efficiency program significantly reduces energy use and greenhouse gas impact in buildings.
Leadership Energy Environmental Design (LEED)
Our campus, a young but rapidly growing university, has had a unique opportunity to ensure all buildings are designed and constructed to achieve environmentally sustainable standards.
A commitment was made early in the development of the campus, that each building constructed would achieve a green building standard. The university selected the US Green Building Council (USGBC) Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) certification.


LEED-NC certification ensures that a building's design and construction strategies achieve sustainable standards and include but are not limited to, maximized energy savings, emissions reductions, water efficiency, and improving indoor environmental air quality.
LEED silver was the minimum certification standard for the campus until 2009 when the university established LEED gold certification as the minimum requirement. To date, the campus has a total of 24 LEED-certified buildings (12 Platinum, 8 Gold, 1 Silver, and 3 LEED EBOM certifications 2 Gold, 1 Silver).
Did you know: in 2006 the campus participated in the USGBC portfolio pilot program to help guide the development of the application guide for Multiple Buildings and On-Campus Building Projects. The application guide provides direction in applying LEED Green Building Rating Systems into new construction and major renovation projects for multiple building settings and campuses. The campus has worked to demonstrate sustainable systems in buildings while also serving as a resource for other institutions to implement sustainable practices that can reduce emissions.
California Energy Code Title 24
Title 24 sets building energy efficiency standards in the state of California. The campus, through aggressive conservation measures designed buildings to consume half of the energy and demand of similar university buildings in California, surpassing Title 24 minimum efficiency standards by 20 upwards to 50% for buildings.


Did you know: pass revisions of the energy code for the state of California were updated because of advancements made by UC Merced, specifically lighting control methods designed into buildings, which included multiple controlled lighting systems, occupancy sensors, and lighting control management systems.
Whole Building Energy Performance Targets
Benchmarks have provided a baseline for all of a building's energy load, and not just load requirements regulated by the state of California. UC Merced has used whole building energy performance targets since it's founding. The targets are percentages of an established baseline that buildings are designed to perform to, increasing a building's energy performance.

These commitments were among the first steps taken by the campus to reduce the university's carbon and environmental footprint.
Energy Efficiency Retrofit
To reduce emissions the campus will continue to install and prioritize energy-efficient retrofit projects throughout buildings. In 2019 electricians did a LED street lighting retrofit totaling 49 light fixtures. LED retrofit on the high bay lighting on campus SSM totaling 22 fixtures. The campus has also retrofitted CTK Quad LED 57 exterior lighting fixtures, and recreation building lighting fixtures.


Education Strategies
Our education programs encourage students to learn and share knowledge about carbon emissions and sustainability. Student projects have focused on climate energy education and have assisted faculty research through the Energize Colleges Program and the UC President's Bonnie Reiss Carbon Neutrality Initiative program a program funded and supported through the UC Office of the President which provides support and funding to students.



Project topics have included, but are not limited to;
Research on carbon sequestration and offsets, building energy analysis, climate action plan updates, ASHRAE audits, biomass gasification, energy, and environmental management and research.
Energize Colleges
Energize Colleges program is a partnership with Strategic Energy Innovations (SEI) to advance energy and sustainability education and workforce development through experiential learning. The Energize Colleges Internship Program allows students to gain real-world experience by contributing to meaningful projects related to sustainability.
The three goals of the Energize Colleges Internship Program are to:
- Develop student awareness, knowledge, and behavior associated with sustainability concepts including energy efficiency, distributed generation, demand response, water efficiency, decarbonization, and zero waste.
- Develop students' technical skills and career readiness by providing training, hands-on experience, and work and/or internship experience.
- Provide resources and mentoring to increase students' access to and participation in sustainable careers.


Energy
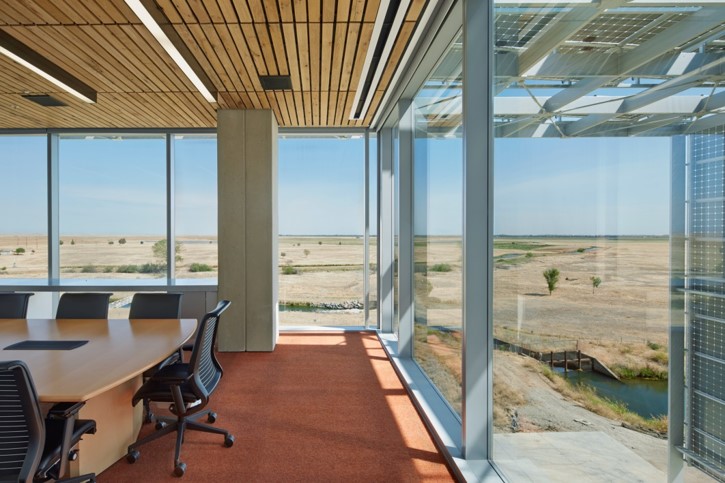
Onsite Renewable Energy Generation
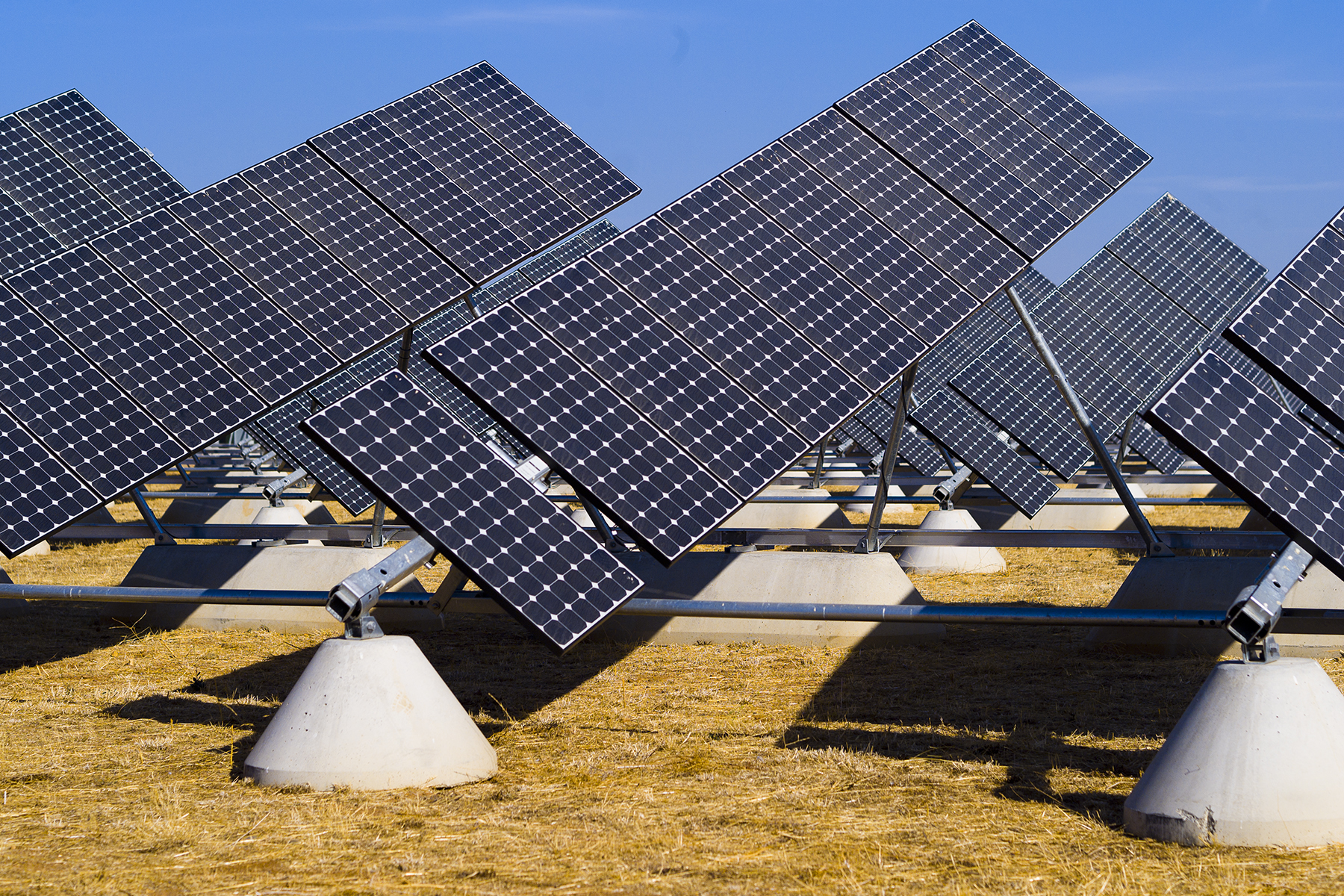
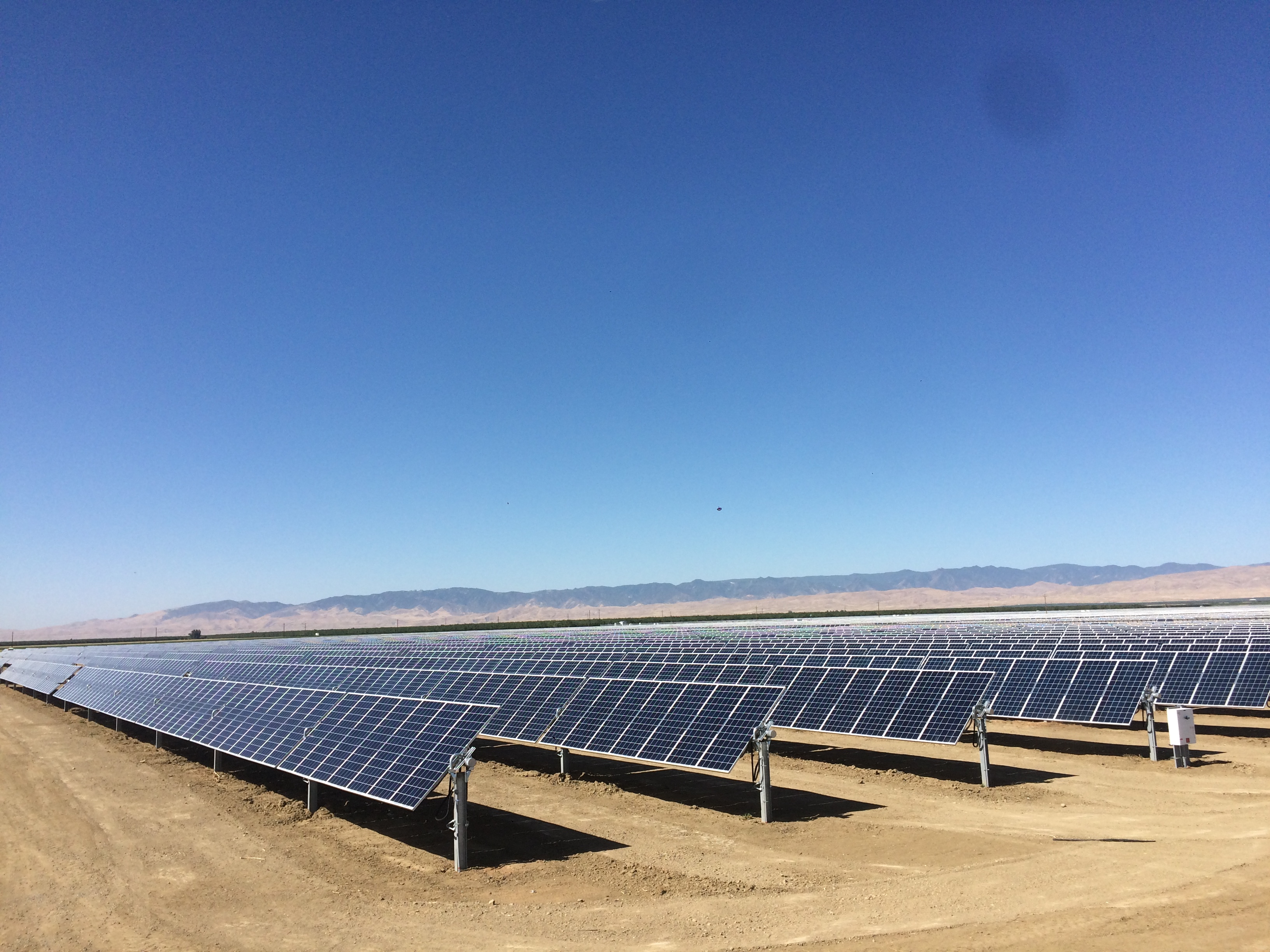
A key strategy for achieving carbon neutrality is renewable energy generation on campus. Renewable energy from sources like solar do not emit carbon and supply the campus with clean electricity. UC Merced has solar systems powering the campus, including a one-megawatt ground-mounted system ins and a five-megawatt carport solar system with battery storage. Both systems translate to significant energy cost savings.
The T-20 ground-mounted system tracks the sun's movements and features 4,900 solar panels on 8.5 acres. UC Merced's location in the sunny San Joaquin Valley makes it an ideal location to set up and study solar energy projects. This system also allows faculty and student researchers to collect data to help explore and create solutions in solar energy.
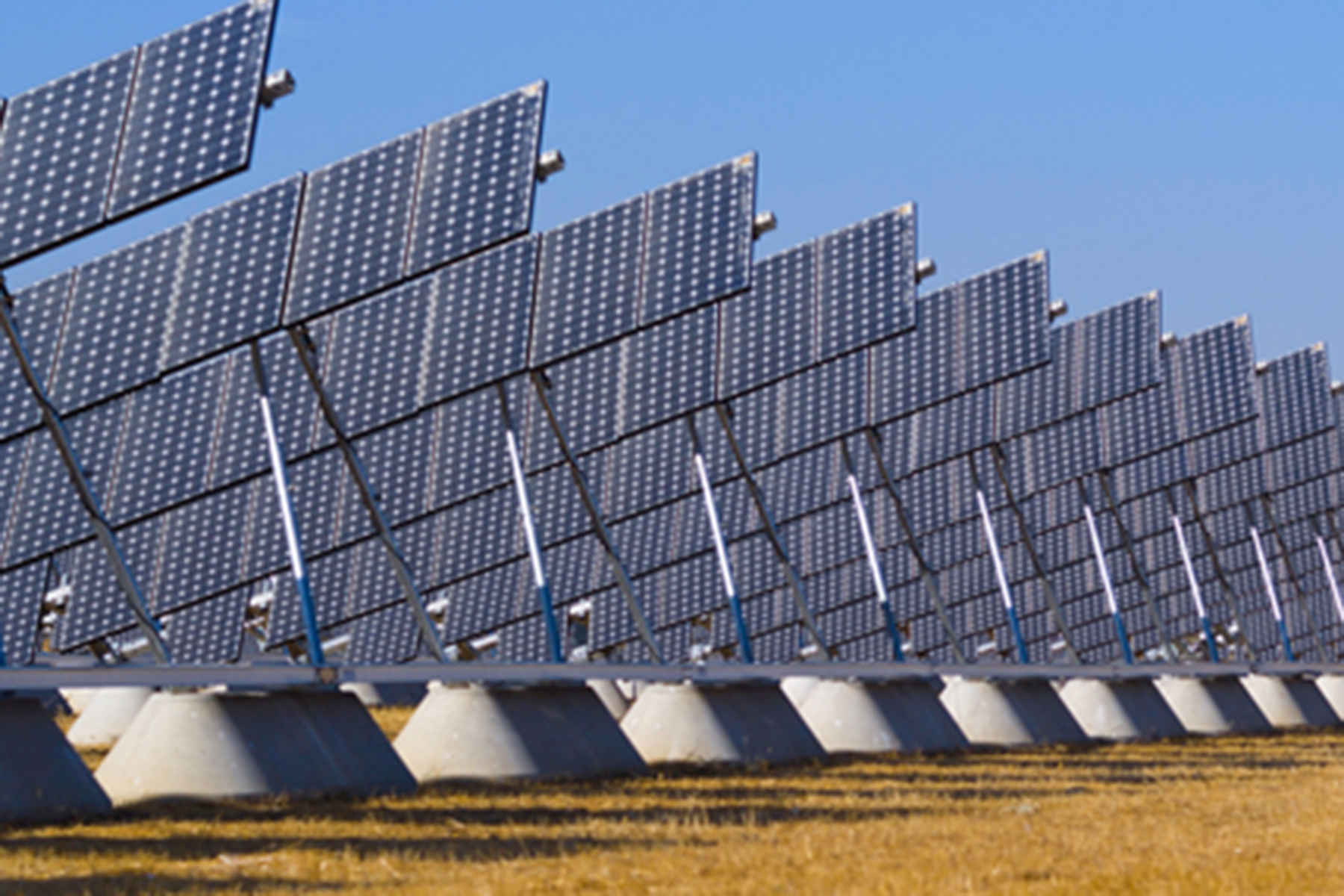


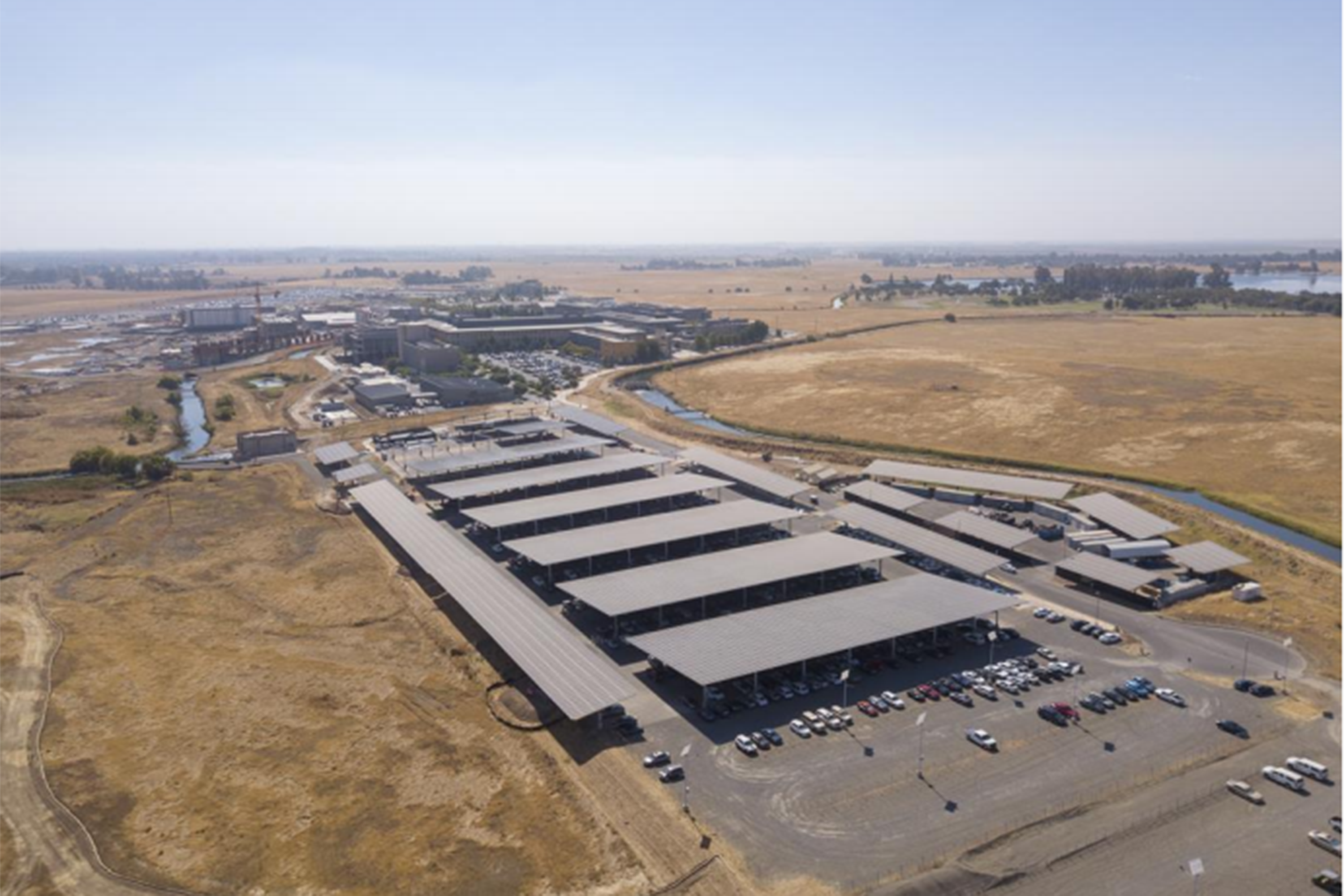
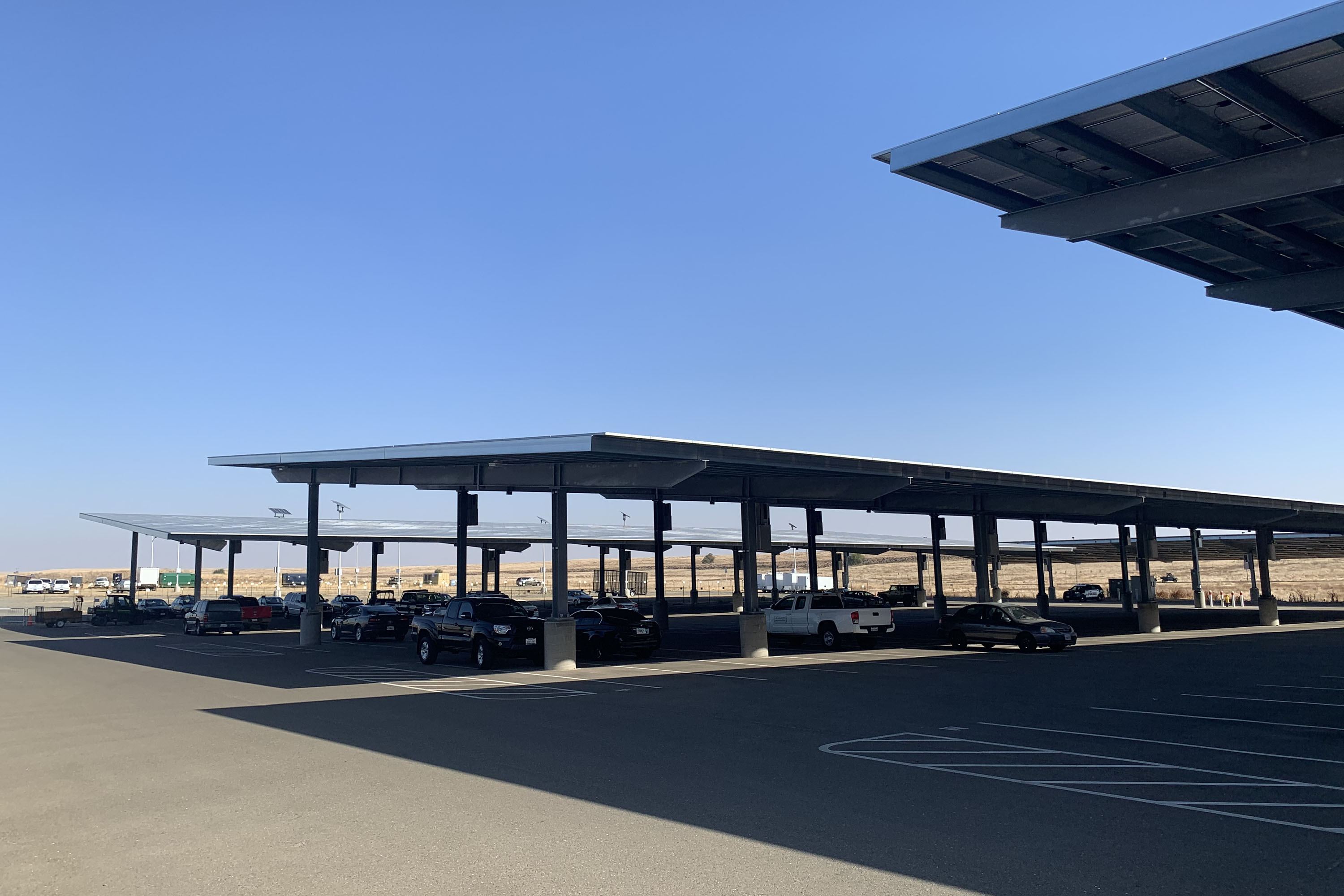
The five-megawatt carport solar system features over 10,000 panels and is coupled with 500-kilowatt energy storage. The system generates clean electricity equal to removing approximately 30,000 cars from the road every year. The carport design of the system allows vehicles to be parked underneath; providing shade from the sun, while also generating power.


Sourcing Clean Power
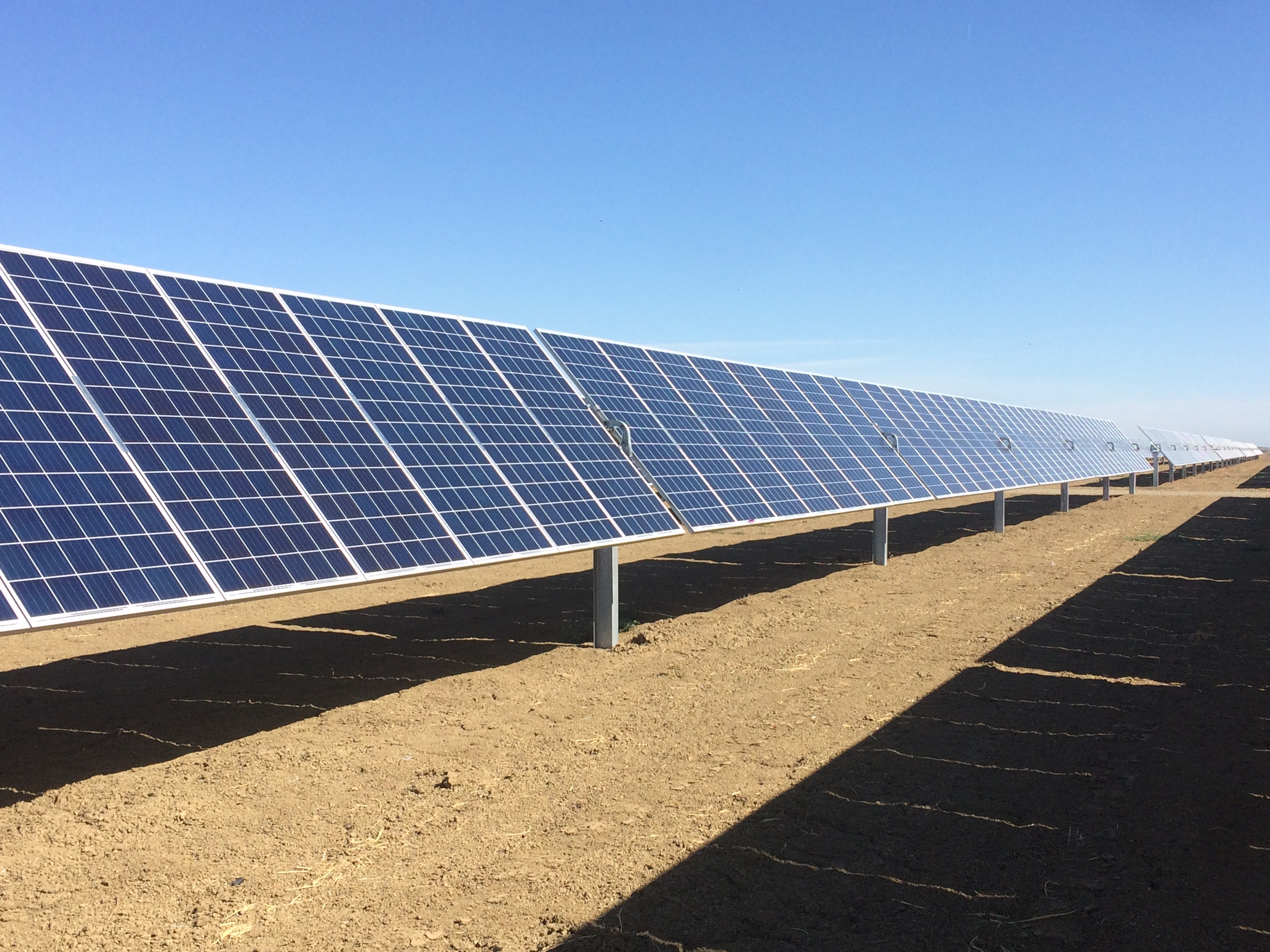
The university began participating in the University of California System Wholesale Power Program in 2015, a strategy that has allowed the campus to source and purchase clean electricity. The program makes up a significant part of UC Merced's energy portfolio for carbon neutrality strategy achievement.


More Projects
The campus is exploring several projects to increase its renewable energy generation onsite. This includes more onsite solar to accommodate energy consumption as well as local partnerships to source landfill gas to reduce natural gas use onsite through combined heat. These complex projects are still ongoing. The campus is also exploring micro grids, solar thermal, and RE system demonstrations with faculty on the campus.


Transportation
The fleet services unit developed a "Right Size Fleet Program" that has worked with several departments to identify specific vehicle needs. As a result of the program campus departments purchased electric golf carts as alternatives to sedan sized gasoline consuming vehicles. The program has supported reducing greenhouse emissions output. Fleet services will continue to steer departments to alternative fuel vehicles when the use allows. Additionally, the campus will continue to promote alternatives modes of transportation to reduce emissions.



Offsets
Offsets have been a strategy the campus has taken to reduce its emissions profile. The single greatest generation of emissions at UC Merced to date comes from natural gas use onsite. Strategies the campus is taking and working towards to reduce the need for purchased offsets includes, identifying an alternative clean energy source for natural gas, increasing energy efficiency on-site, and developing infrastructure that moves away from the need for natural gas. In fact, the University of California System policy specifies that new buildings and major renovations will not use fossil fuel combustion for space and water heating. The campus is also exploring opportunities to collaborate with faculty members to create offsets internally developed through projects that the campus can use.
Research
UC Merced’s world-renowned research is at the core of the university’s mission. Not only is the campus implementing practices to reduce its emissions, but the research initiatives, institutes, and centers also address an array of complex issues on climate change. Carbon emissions reductions are one avenue that can directly impact climate change but the research initiatives, institutes, and centers noted below highlight the realities of a changing world, what to think about and anticipate when navigating new realities.
The Faculty Advisory Committee on Sustainability (FACS) is an initiative of the Faculty and Provost's office that acts to encourage and support sustainability education and research across all constituencies on campus.
The Sierra Nevada Research Institute (SNRI) at UC Merced discovers and disseminates new knowledge that contributes to sustaining natural resources, and promoting social well-being, facilitating synergistic links between science, the arts, education and natural resource management, and focusing research on water, soils, forests, and air quality.



The University of California Advanced Solar Technologies Institute, also known as UC Solar, is a multi-campus research establishment dedicated to the generation of state-of-the-art solar energy technologies, the examination of solar energy economics and policy, and the development of technologies that make solar energy systems more efficient and affordable.



CITRIS was created “to shorten the pipeline” between world-class laboratory research and the creation of start-ups, larger companies, and entire industries. CITRIS works to find solutions for many of the concerns facing society today. Those include monitoring the environment, finding viable, sustainable energy alternatives, and simplifying healthcare delivery.”






